All about the Dark Side of the Moon: Unraveling the Enigma
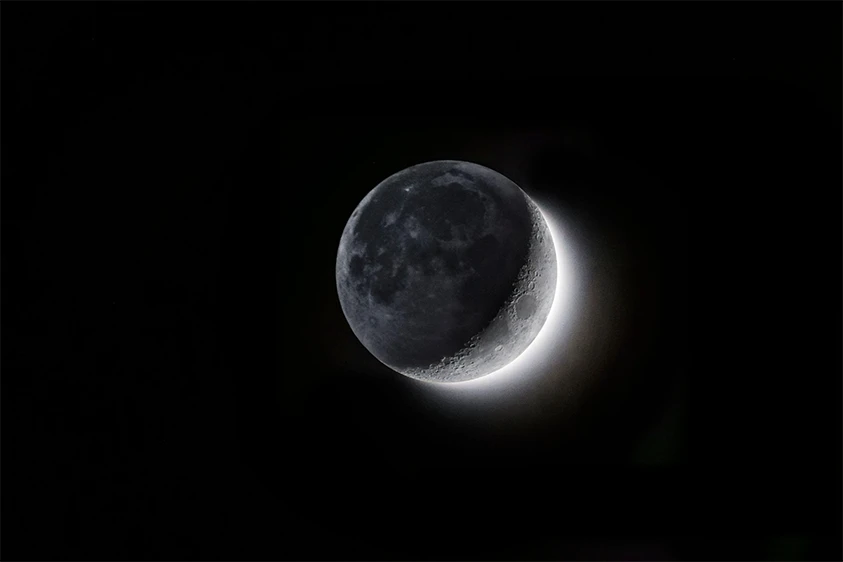
There is something special about the moon, and the concept of its side appeals to many people. It is also a myth. On the contrary, there isn’t a ‘this face of the moon’ and an ‘other face of the moon’. In this case, there is a side that is not visible from the Earth and is usually called the “dark side.” The Moon’s rotation over time and its gravitational interaction with Earth cause different sides to be exposed to light as the Moon orbits around the planet.
The moon takes 27.3 days on its own axis to get through rotation, which is similar to the time it takes for the moon to make an orbit around the Earth. This event, which is known as mutual locking, makes the lunar surface appear sunlit from our viewpoint on Earth. The part of the moon that faces us is the one called the near side. This shows phases of the moon, from the new moon to the first quarter, then the half moon, and ending at a full moon. Throughout the cycle, the moon’s illuminated surface reveals or conceals parts of itself. However, the same side of the moon we see all the time is invisible as well. Takes exactly the same amount of time to turn around.
Common Misunderstandings Regarding the Dark Side

General Misconceptions
The “dark side of the moon” myth is based on the perception that there is a side under the shadow, which is very far from the truth. Nevertheless, that is inaccurate. In truth, both the moon’s sides, however, have their periods of daytime and nighttime, although it is orbiting around the Earth. The word “dark side” is used in music, and this phrase contributes to the impression that this is the actual. The second myth is that the dark side of the moon holds countries or land, when the true picture is that there is no land in such a moon.
Libration is the word used to describe all the phases that the moon goes through during its orbit around the earth. Consequently, telescopes view over 50% of their surface, despite the fact that one side endures facing forever towards Earth.
Misconceptions about Exploration
A common myth among many is that no space agency, such as NASA, has set foot on the surface known as the dark side of the moon. On the other hand, a terrific fact is that while no human has ever touched any part of the moon, robotic vehicles and telescopes have been carrying out research concerning this objective.
To cite a few examples of missions that have skillfully investigated the back of the moon, we can mention the Luna 3 probe launched by the Soviet Union in 1959, which managed to retrieve and transmit pictures of this territory, as well as the Chang’e 4 mission conducted by China in 2019, which efficiently landed a rover on the far side for scientific aims. Thus, scientists, after all, owing to those cases, decided to pay attention to and extract useful information from that shade of the moon, which is named the dark side.
Importance of Scientific Exploration

Considering NASA’s roles in the investigations of this area is crucial because. The astronauts of NASA’s astronauts are the humans who actually saw the horizon because they view the side of the world, and as far as the one who is outside of earth, we regard it as the dark side. In addition, significant attention is put on studying volatiles in samples, such as the relation between their abundance, distribution, and sources, associated with the moon in particular.
Role of Lunar Reconnaissance
One of the instruments used for exploration is the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter by NASA (LRO). The mission of this space machine has been to supply scientists with sensational pictures and vital documents about the Moon’s surface at large, with a specific emphasis on the little-known far side. The LRO was purchased by NASA and has sent back many pictures of craters, basaltic plains known as Maria, and other fantastic features on the moon surface. Histories of the moon and its evolution are researched with the help of these images.
Other Spacecraft Missions
Besides NASA, other space agencies, in like manner, have facilitated navigating the charted parts of the moon. Nations with spaceflight enterprises have harvested data to enlighten our minds concerning this tangled lunar area. Similarly, the Center for Lunar Origin and Evolution addresses the South Pole-Aitken Basin, the largest impact basin, which is an arc that starts near the south pole and takes up an enormous area in the southern hemisphere on the far side.
You might have to immerse yourself in the studies of moon side information, but science as a whole continues to discover new things. One of the most prominent achievements of moon missions is that our knowledge about the formation of the moon is much more in-depth, and this information may be used for future explorations. Stay up-to-date by reading up on lunar discoveries and always maintaining a positive attitude. You will learn about how this captivating celestial body functions.
Astronomical Concepts
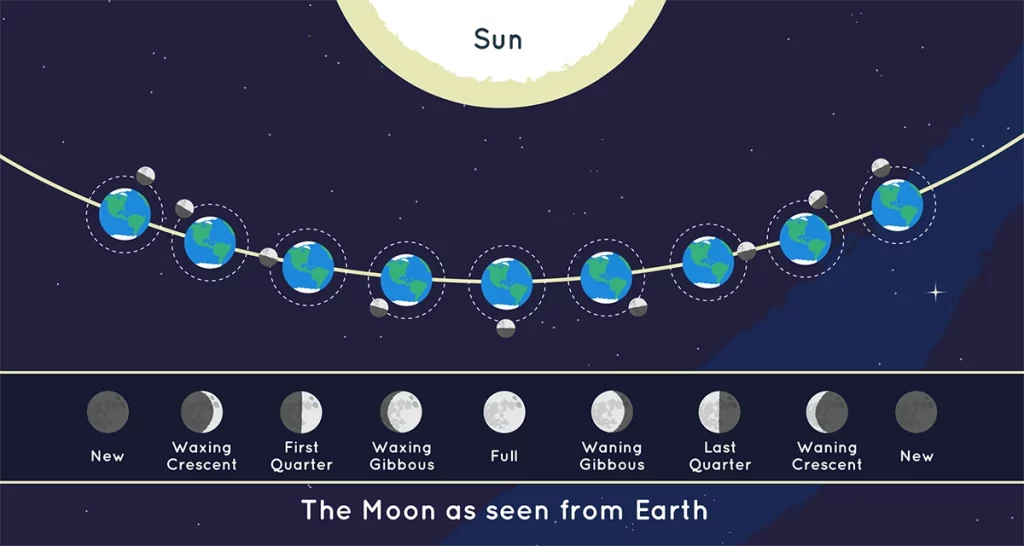
Orbit of the Moon
Learning about the side of the moon starts with getting a grip on what its orbit is. The moon orbits around the Earth and takes about 27.3 days to complete one lap.
When the moon starts to move, it is under the influence of both the sun and the earth. Due to this, a certain part of the moon, which is called the near side, is facing the earth all the time. The other side, also known as the dark or sometimes dark, is not visible from Earth. Nevertheless, dark and light sides receive as much sunlight as the other; therefore, the actual darkness is irrelevant.
Moon’s Rotation
Besides the moving of the moon around its axis, there is more to the meaning behind one side and the other. Its rotation period is quite similar to its orbital period of about 27.3 days to complete one rotation. This synchronization between the moon’s orbit and rotation, in which we can see only one face of the moon from the Earth, is what makes the moon our natural satellite. This phenomenon is accordingly named locking. It happens because the gravitational force between the earth and the moon is growing stronger and gradually slowing down the rotation of our planet, making it permanently locked in fixed-position synchronization.
Lunar Phases
The moon features distinct phases that help us spot the half of the moon that most often goes unnoticed. Similarly to the orbital movement of the moon around the earth, its specific location with respect to the sun and earth alters the amount of sunlight that gets to its surface. This results in phases:
- New Moon: The side of the moon facing Earth is not exposed to the light of the sun. It seems to go unnoticed.
- Waxing Crescent: The camera slowly shows a little bit of the side. Gradually grows larger.
- First Quarter: Half of the side can be clearly made out.
- Waxing Gibbous: As a side note, more than half of it is on view.Continues to grow.
- Full Moon: The whole side will appear to be lit.
- Waning Gibbous: The dark side, kept in the shadow, begins to appear.
- Quarter: Now only half of the side is visible again, but on a different from the side that was visible before.
- Waning Crescent: To be specific, only a small fraction of the illuminated side of the moon is observable until the next moon phase has a rise.
While every lunar phase is unique in showing an ever-changing pattern from the lighted to the dark parts of the moon, which is generally believed to be “the dark side” of the moon, This may be a strong clue that it’s far from a place in the dimness. An explanation of the idea of tides and tides would provide a valuable base for the unwavering and precise speeches about this feature of the moon.
The Moon’s Influence on Earth

Our planet Earth is the unique planet in our solar system, which also has another natural satellite called the moon, which is the fifth largest one among all the moons. Interestingly, whereas the moon cannot produce light of its own, it sure casts some remarkable effects on our lovely planet.
Tidal Forces
The Earth’s oceans are being pulled by the gravity of the moon; therefore, they’re either getting higher or lower at the same time as the moon. In the process of the moon’s orbiting our planet, the gravitational force pushes the oceans away from it to form a bulge, which is where the oceans are nearest to the moon. Along with the visible bulge, the same is there on the opposite side of the earth. These rhythmic lumps cause a high tide and a low tide, too.
Eclipse Events
The moon’s orbit around Earth results in solar and lunar eclipses. This phenomenon happens because of the alignment of the moon, Earth, and the sun. A solar eclipse is a phenomenon where the moon fuses between the earth and the sun, making the sun invisible to us. Nature is funny. Lunar eclipses form when Earth blocks the sun’s rays and causes the shadow of the planet to spill onto the moon’s surface.
Additional Effects
- As well as being a balancing wheel, the moon also serves the purpose of averting the earth from the process of rotational axis motion drift. This offers climate stability for as long as a period of thousands of years.
- Certain experts also believe that the moon, with its gravity, could help early life develop on Earth as well.
- The moon was understood to have been the causative agent behind small lake-like tremors and earthquakes witnessed on the surface of our planet.
Moon compared to Earth
| Feature | Moon | Earth |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | 3,474 km | 12,742 km |
| Mass | 7.3 x 10^22 kg | 5.97 x 10^24 kg |
| Density | 3.3 g/cm^3 | 5.5 g/cm^3 |
Even though the moon is only a little similar to the Earth, it has created many conditions and events across the surface of the Earth. As astronauts cross indifferent time or space, the amazing stories of the universe and the past and future of the solar system are exposed gradually through astronomy’s ongoing study.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes the far side of the moon unique?
The far side of the moon, which is also known as the “shadow” side, is distinct from its near-side counterpart either in terms of composition or appearance. It is characterized by a crust and more impact craters because of volcanic activity. Surprisingly, it gets as much sunshine as its nigh side.
Why is it that we can never see the side of the moon from Earth?
The side of the moon facing away from us has no light because of a phenomenon called locking. This implies that when orbiting Earth, the moon rotates on its axis at a speed that is fast enough to cause only one side to be permanently visible to us.
Has NASA ever explored the side of the moon?
Absolutely! NASA explored these regions, too. In the 1960s, the Lunar Orbiters showed the lunar surface for the first time. Nowadays, we have technology like the one on the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, which has allowed us to get images of very good resolution and information about the moon’s geological formations.







