25 Turning Points in Earth’s History That Formed Our Planet’s Past and Future
Through millions of years of the social history of our planet, there have been periodic changes that have made our planet into the unique multi-purpose habitat we know. This article will cover twenty-five of the events that changed the course of our planet. In this article, we will focus on twenty-five events that have changed the fate of our planet since the very beginning until now. This understanding, along with a sense of appreciation, will be boosted as you read so that you can follow the long way the Earth negotiated through time and understand how the events influenced life as humanity knows it today.
Through this writing, one will inscrutably understand the extent of the biological changes that our planet has experienced. From the moon formation to the tragedy of Triceratops and the creation of humankind, every effect has shaped the cosmic journal. Moreover, you will learn that perceptions of the impact of these events on Earth and its people change with time and what vicinities they have for the future of Earth.
As you move on and look at these 25 events in particular, what you will learn is both the ever-changing and the stable features of our planet, but at the same time, you will develop an appreciation for them because of their determination and readiness for each new event. In the meantime, you become aware of how things interrelate with each other and what role is assigned to us humans to decide responsibly and to be stewards of our world.

Creation and Formation of Earth
The story of how the earth came to be started around 13.8 billion years ago with the big bang, which is the stage on which we are witnessing the universe. In our space-time continuum, 4.6 billion years ago, our “home” ground, the planet Earth, began to emerge.
In the solar system’s early phase, a cloud of material elements emerged. Gravity compounded the creation of these materials into a process that led to the formation of planets, of which Earth is one. The process through which this takes place has a name: accumulation. May have been the marker of the first day of the creation of the earth. Create an intelligent and faithful translation using the interactiveparaphrasingtool.com online platform.
With a click, let’s land on the timeline of the earth’s formation. The time span required for the Earth to reach its current size from its very first stages is 10–20 million years. All the previous heating and collisions generated at extremely high rates by decay processes made the early planet molten. Thus, the liquid-metal phase contributed to the formation of the core at the center of the planet, where heavy metals are located, and the surface layers, which are made up of lighter elements.
Since the beginning of this process, changes in the terrestrial atmosphere and lithosphere have been happening. H2O is also an important factor during the formation of the first living organisms. Water existed on Earth during its stages, which was the cause of the genesis of oceans, where millions of organisms were sheltered and life evolved.
Understanding in full the character of the Earth in the depths of the universe is only possible by going back to its birth and the most impactful moments of its history.

Atmosphere and Oceans
Communication between Earth’s atmosphere and oceans has become a major factor that has conditioned the environment of our planet throughout its entire history. The presence of ammonia, carbon dioxide, and water vapor dominated the earliest atmosphere. Along with the evolution of time, the emission of oxygen by the photosynthesis of the first living organisms in the atmosphere has made it into the type of environment that we now know.
The structure and dynamics of the atmosphere underwent profound changes, and even its intimate connections with the biosphere were affected. A delicate relationship between the air and the ocean exists, which involves the transfer of carbon dioxide between them. This experience is also how ‘Earth’ is kept in equilibrium.
Weathering, caused by actors, is the main factor behind redesigning the Earth’s atmosphere and oceans. Under the carbonation process, carbon dioxide is extracted from the atmosphere, and at the same time, dissolved minerals such as plankton get introduced, making the oceans habitable. Moreover, it also doesn’t deserve to be ignored that the moon greatly affects the oceans by creating tides, currents, and other different oceanic phenomena.
The shared history of the atmosphere and the oceans of your planet, where each one has affected the other at every stage of time, adds to their influence. The interdependence of these aspects is crucial in gaining a deeper comprehension of our origin and the process of our world formation.

Hadean and Archean Eons
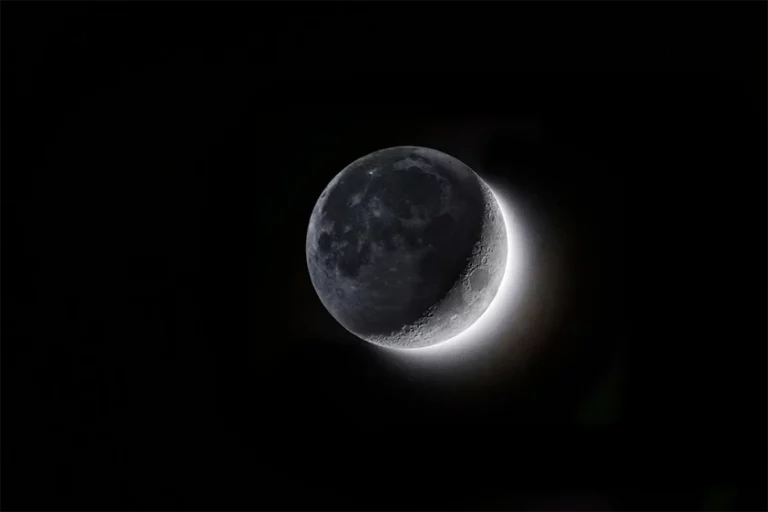
So let’s travel to the Hadean eon (4.6 billion to 4 billion years ago) now. In the days when Earth was gradually birthing its different forms, It was a thermal river of rock. The lack of conditions led to the nonexistence of any form of life in this universe. Interestingly, during that time, the Moon came into being about 4.5 billion years ago, being one of the things that ensured the emergence of the solar system.
The Hadean time went by, and the crust of the earth was slowly cooling down and solidifying. Close to the end of this period, indications of an existing surface on Earth became quite visible. Yet, geologists may also face difficulties associated with the lack of rock samples from those time periods in their study of the ancient Earth. Known rocks, which are on our planet nowadays, date back to the Archean eon.
The Archean, which is considered the eldest part of the geologic time scale, is a time period in which Earth’s crust was getting more and more expanded and thicker.
The primordial Archean era, an eon in Earth’s history, presented some of the earliest clues indicating life existing on our planet. During this period, eroding processes like erosion, which formed the land masses, became the prerequisites for life development.
If you were a geologist with that specialization, your gear would be studying minerals and rocks to solve the environmental conditions many billions of years ago on Earth. Among your tasks would be going through these stones in order to find such microorganisms as bacteria, which are preserved there.
The Paleoarchean and Hadean eons contributed to the development of the Earth on a wider scale. The truly remarkable phase in the history of the universe that was accompanied by the formation of our planet contributed greatly to the diversity of our ecosystems.
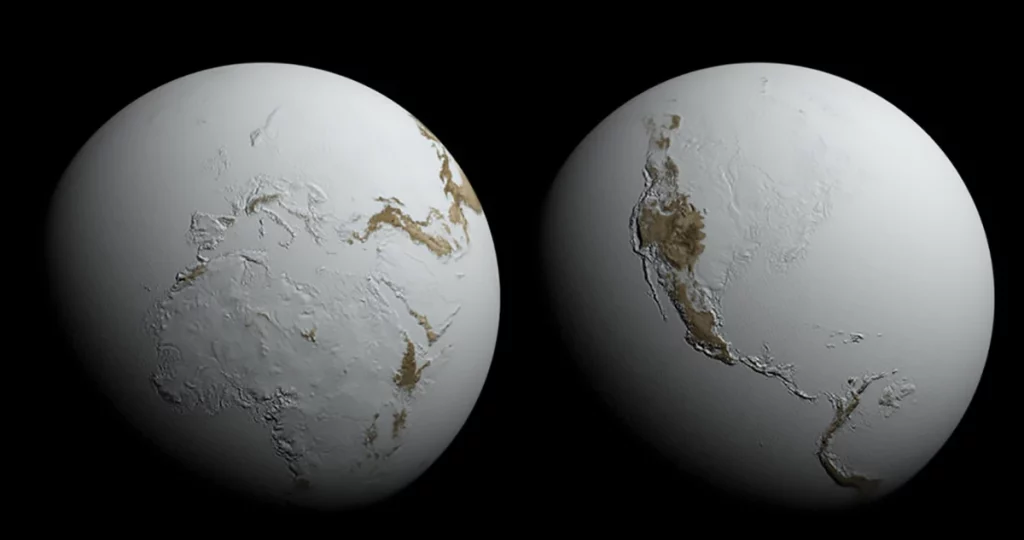
Proterozoic Eon and Snowball Earth
The Proterozoic Eon that transpired between 2.5 billion and 542 million years ago was the crust and also took place during environmental transformation. During this era, there was a transfer of oxygen from water to air, which was one of the noteworthy things that happened.
All the time, the cyanobacteria, through photosynthesis, were a part of a process that kept on producing oxygen through their metabolic activities. This oxygen accumulation was followed by the emergence of the ozone layer within the atmosphere of the Earth, which assisted in blocking ultraviolent rays and supporting the evolution of life on our planet.
In addition to high O2 levels, the planet had several ice ages, including glaciation periods during which it looked like the Snowball Earth. Those events consist of the nearly entire one-layer of the Earth covered by glaciers, which reshaped ocean circulation and the carbon cycle. Consequently, oxygen levels dropped terrifically, causing many extinctions and forming the foundation of the evolution arc for life on our planet.
The methane in the air was believed to have dropped its levels during the part of Snowball Earth history as it was converted into carbon dioxide by its interaction with the rising level of oxygen in the atmosphere. Methane, a greenhouse gas, was responsible for warming during this time, and the failure of natural processes to produce new methane led to a compounding effect of less overall warming and more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This likely influenced the cooling and the spread of glaciers as well.
With the carbon cycle starting to function, your planet would be leaving the glaciation period. Having switched the climate to a moderate one, This is how the likes of plants, animals, and other multicellular life forms developed during the next era, dubbed the Phanerozoic. Throughout this time, life on Earth showed extraordinary development and a lot of biotic diversification.

Cambrian Period and Explosion
The Cambrian Period, which began around 451 million years ago, brought about numerous changes. It was about this time that a predictable thing happened: an explosion. This is the prolific diversification of marine species. In just one million years, the formation of a myriad of complicated life forms, which you are so familiar with today, started.
The Cambrian Explosion led to diversity and complexity within various ecosystems. The predecessor of this period, known as the Ediacaran one, was a time of primordial life with tiny organisms, giving way to more evolved ones. The dawn of predation and competition later triggered the evolution of shells, spines, and other defense mechanisms.
The progress of visual apparatus is also a significant event during that phase. Along with the apparition of organs, the vision of living creatures also improved, helping them to exist. This gave an edge to species that were capable of identifying predators and locating food, leading to the evolution of large-eye creatures over time.
Sometime in this epoch, a happy life prepared the groundwork for life as we have it today. The evolutionary process saw diverse organisms becoming the ancestors of the existing regions of arthropods, mollusks, and other significant groups. After the specified time, almost all the modern groups of animals were part of the earth’s ecosystem.
To sum up, the Cambrian period and explosion are events that took place in your planet’s history. The formation of living organisms at a fast frequency, adaptive modifications, and marine biodiversity have together shaped our world. Provided the basis for all existence in the future.
Through the course of our Earth’s existence, life has experienced various revolutions, resulting in multi-faceted processes. Probably one of the most significant components of the trip is a formation called the biosphere, which contains all the known living organisms. Actually, it was that biosphere from which the extraordinary diversity of life we enjoy right now evolved.
One must understand that the role of organisms is profound regarding the evolution of life. These are considered to be the most ancient forms of life, called prokaryotes. Microbes are their popular name. In the course of time, the gaseous exchanges gradually changed the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere in a special way by means of photosynthesis, a process of receiving energy from the sun and turning it into chemical energy. This metamorphosis became the crucial fact for existence and the consequent accumulation of oxygen in our atmosphere. This implied a decisive moment. This event opened the gates to the era known as the Phanerozoic eon.
This phanerozoic eon began 541 million years ago and extends to today’s world. It is in this epoch that the development of more multicellular organisms complex enough to form massive colonies is seen. During this era, as well, the forms of plants got more and more complicated. By sifting through this era, plants had to inhabit extremely different environments; they went from developing vascular systems to embryos and then colonizing terranes, and water-based habitats left them behind for good.
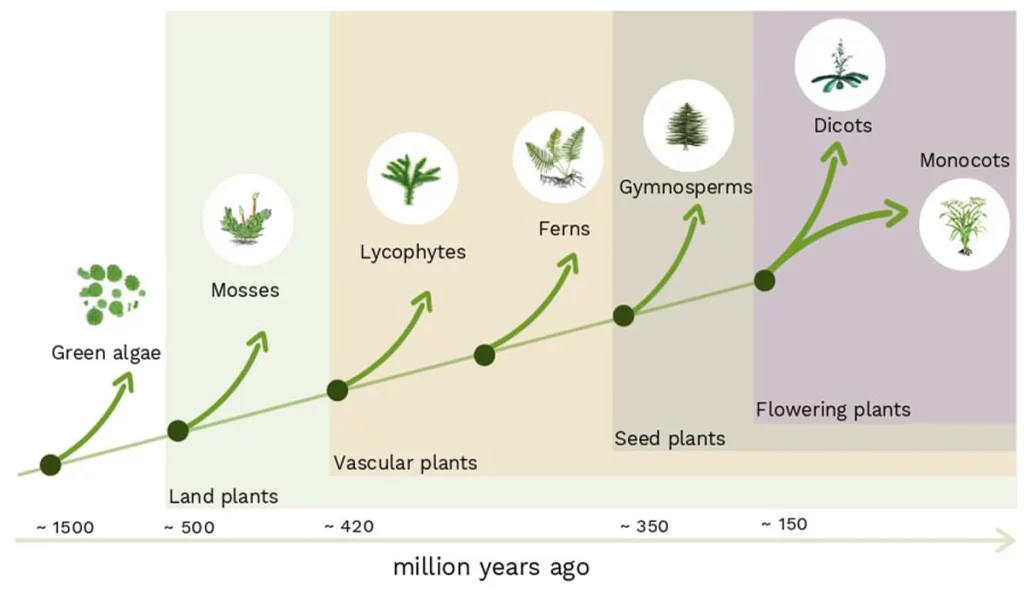
evolution of plants
A prominent event in the course of plant development was the time when vascular plants came into the foreground. These plants evolved with the help of tissues that were named xylem and phloem, which helped them circulate nutrients and water they had through their entire structures. Adopting this trait enabled plant life to grow higher and taller; hence, sunlight reached and the plant photosynthesis rate became greater.
After the evolution of plants, it was time for the seeds to develop. The seeds of the angiosperms, or gymnosperms, are the most precarious stage for the seedling because they are terminally dependent. This advancement gave rise to two groups of plants: both gymnosperms and angiosperms. The evidence is the Gymnosperms, which, at least conifers and cycads, produce exposed seeds to the environment. Angiosperms (among the other plants) produce seeds that are borne inside fruits. As you have a look at the developed world of plants on Earth, you can see angiosperms are the largest represented group.
Minority might be right that through the constant contact of microorganisms with plants, the roots of the current biosphere were laid. Since the time of photosynthesis, which creates energy in plants to form disks and seeds that evolve, plants on Earth have displayed wonderful, grateful truth. It will not be any wonder to see the branching of mechanisms that have gradually made plants successful as they enter your mind.
The evolution of animal life on Earth has had a very enchanting history, which can be divided into different eras, marking the turning points of the journey. Our excursion will start with a look at the space inhabited by invertebrates, then proceed to the succession of vertebrates and the whole process of the evolution of species, including mammals and dinosaurs.
At first, the first organisms were flattened primitive animals such as sponges and jellyfish. The predecessors of present humans were those that had those particular bodies, and they were among those who lived in Earth’s seas without any spine. In due course, invertebrates evolved and created new genera, thereby originating a wide variety of types of creatures, among them echinoderms, mollusks, and arthropods.
Last but not least, 500 million years before the present, creatures with spines appeared and embellished life on Earth. Beings with backbones had gained a vast amount of flexibility, which in turn allowed their survival and movement in a way that had never existed before. The most archaic vertebrate skeletons amongst the first vertebrates that existed aped what resembled fish, the Haikousichthys ones. They survived and, later on, diversified to become kinds that could linger on in the oceans.
Advances within the Mesozoic Age were when the era of dinosaurs was officially introduced. Those archaic reptiles continued to reign supreme until the appearance of other species that occupied the ecosystems of the whole planet. A trace of them is in the fossil record.Showcases their remarkable diversity.
Sadly, the era of dinosaurs was over 65 million years ago, at a time of mass extinction. On the other hand, the extinction of dinosaurs opened up evolutionary niches for mammals to fill. With the climate changing and some habitats being formed, mammals grew into species that were comfortable in whichever environment they had adapted to. It was only possible, as a result of it, that they managed to survive and form life on Earth.
When one explores the wide range of animal species on Earth currently, it’s mind-blowing to know that all those creatures did not appear overnight, but rather, they have been on a long journey. From invertebrates to dinosaurs and then to mammals, each age has played a part in the detailed design that we have all around us.
Climate change and mass extinctions lead to the alteration of Earth’s progression. These events are, as a rule, the consequence of meteorites, asteroids, or climate change-caused disturbances and lead to one of the patterns of species disappearance. Nevertheless, they also have the potential for less-favored variations of life to come about.
Among those well-known worldwide is the one that took place near 66 million years ago, when a huge meteorite hit the Earth. A catastrophic event that eventually led to the extinction of dinosaurs. Ultimately, this meant mammals were able to dominate and develop. In other words, the last extinction, referred to as the Cretaceous Paleogene event, occurred with about 75 percent of all life-form species gone. With the presence of climate change, large extinctions have persisted in history.
Nearly 443 million years ago, our planet underwent a massive catastrophe named the Ordovician-Silurian extinction. This is an event that is caused by changes in temperature and leads to the loss of 85% of sea species. Much like 251 million years ago with the Permian Triassic extinction event. The most likely cause is believed to have been a result of volcanic activity, climatic change, and the freeing of methane. Surprisingly, this event resulted in a 95% diversity decrease in aquatic organisms. It becomes known as the Great Dying, one of the worst extinction events in the history of our planet.

Meteorites and climate changes
Likewise, with the understanding that meteorite impacts and climate change are the most common causes of mass extinctions, there are other factors that can contribute to the same phenomenon. For example, during the Triassic Jurassic extinction, which set in around 201 million years ago and is believed to have reduced the number of living species by up to 80%, the mass volcanic eruption showed great effect and changed life on our planet. This event was especially a turning point for the dinosaurs until their all-time demise during the Cretaceous upcoming years.
This consciousness about mass extinctions and their basic factors can provide us with insights into the challenges that were dealt with in the past (such as current climate changes) and those that are going on now. With such recognition of the wounds deriving from events that happened in the past, we will be able to be completely ready for a crisis situation completely.Potentially mitigate their impact.
On getting deeper into the discussion of plate tectonics, you will come to the idea that the Earth’s crust is a layer on the outer shell of the planet that is made up of quite large plates that are constantly in motion relative to each other. These plates consist of two types: oceanic and continental, which make up the Earth’s surface.
The fact that most of the planet’s surface has been formed by plate tectonics is important to understand in order to get a good grip on how the surface has changed over time. The foundation of plate tectonics lies in the fact that the earth’s crust has been divided into plates that gently move above a layer of liquid very beneath this called asthenosphere. This is done as materials from inside the earth go up and get a solid crust that is referred to specifically as silicon and oxygen.
As a result of the plates’ movement, the driving forces originate internally inside the Earth. As heavier things go downward while lighter ones go upward, a system is created that helps develop currents. These conveyors facilitate the horizontal motion of the plates. Furthermore, the axis and the magnetic poles of our planet moving close to the earth make up a varying contribution to these movements.
As these plates interact, you’ll notice that there are three types of boundaries: critical thinking, problem solving, and being creative with real challenges. Divergent boundaries are developed as a result of plates pulling away from each other rather than being pushed forward, which in most cases results in the formation of crust. Convergent boundaries are created when slippery plates collide. Sometimes the slower plate is forced down into the deeper subduction part of the earth, and a trench is formed. Web-boundary motion is characterized by plates sliding past each other, but with stress accumulation and subsequent rupture leading to the occurrence of an earthquake.
The Earth’s tectonics have been essential in building its surface during the planet’s geohistorical process. Tectonic plates are shifted and move about due to the constant interaction, leading to the creation of ocean basins and the rise of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Through the grasp of plate tectonic mechanisms, we spur a sense of knowledge in the process, which in turn formed the earth as it is now.

Changes, in the Solar System
Our system has had its route marked by significant events that tie up with the way it is shaped now. Such incidents are the result of the procedure of creating and making the planets, such as the Earth, Mars, and the Moon.
The impact of the birth of the solar system, which developed, evinces a significant change that has been seen in the system. At each successive stage of evolution, the intensity of the sun was much lower compared with what we see now. The outward brightness of the sun was augmenting as it was undergoing the processes of fusion, the primary sources of its energy being the source of life on Earth and resulting in transformational changes in climate.
4.1 to 3.8 billion years ago, our solar system was going through the process of its creation, and this time was a particularly intense period: the Late Heavy Bombardment, which changed irreversibly the formation of planets. During this era, the rate of asteroid occurrences was on the rise. The dust tail seen in this image belongs to a comet that broke up while whizzing through the inner solar system. It is very likely that these strikes have resulted in shaping the outermost shells and the atmospheres of both planets and contributed to the formation process of our moon.
Gradually, shaping great parts of the moon arose as an effect of continuous collisions, whose result was debris that was generated from these impacts and formed not only our moon but also other cosmological bodies in our solar system. The Moon was created by a collision of a Mars-sized body with our Earth. Therefore, the moon’s formation has direct implications for Earth’s climate and the health of the planet.
The collision between two large chunks of substance has resulted in a measurably substantial amount of debris orbiting this planet. Long the way, this form (material) was forming. What we see today as the moon was created in that act.
Moreover, the migration of the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn as the solar system formed also played an essential role in the shaping of our solar system today. The movements of comets and asteroids were most probably affected by their gravitational influence, since the force of gravity can undoubtedly have a decisive impact on the shape of pathways in space. Thus, it has shown how the system of our objects is built habitually today; besides, this process might have had an influence on cataclysms like the Late Heavy Bombardment.
Altogether, these changes in our system have had a permanent impact on the development and fate not just of our planet but also of other planets in our solar system.

Global Climate Ice Ages
Throughout the entire history of the Earth, our planet has experienced changes in climate that have brought about periods called ice ages. These changes have also altered the landforms and ecosystems of our planet. Also influenced the course of evolution.
Ice. Climate Change: An ice age denotes a period during which the earth goes through cooling, thus leading to the glaciation of huge areas of land. These ice sheets can get up to several kilometers thick. It is worth noting that climate change contributes to the cause of these ice ages.
In these cooling periods, global temperatures drop due to the reflection of the sunlight by ice sheets, and, therefore, such a reflection causes the Earth to cool.
Carbon Dioxide and the Carbon Cycle: CO2 is, in fact, an important factor in maintaining the temperature of our planet. It works as a greenhouse gas that captures heat in the air, making sure our planet is hot enough to support life. The carbon cycle is a dynamic process that circulates carbon in the world’s atmosphere, oceans, and land. Any natural changes in the cycle can lead to cooling or warming.
Cooling is contributed by low levels of CO2 during ice ages. It’s due to the expansion of glaciers and oceans taking in CO2 from the atmosphere, which improves the cooling effect. On the other hand, higher levels of CO2 result in warming through the melting of ice, the release of stored greenhouse gases from ice and the seasonal permafrost, and so on, which further increases the temperature of the Earth.
Here are some important facts about climate, ice ages, and the carbon cycle:
- Ice ages are due to fluctuations in Earth’s orbital movement and its position in relation to the sun. As a result, our planet’s exposure to sunlight continues to decrease.
- Greenhouse gas concentration fluctuations, such as carbon dioxide, are linked directly to temperature changes.
- The Milankovitch cycles, being a sequence of motions produced by the Earth’s movement around its orbit, are a factor in changes in climate and the advent of ice ages.
- Spreading out of mountain-building events and volcanism can result in releasing gases and particles that impact the equilibrium between incoming and reflected energy.
- While reflecting on Earth’s past and future, we should bear in mind that this is a system that undergoes transformation, including climate, carbon dioxide degrees, and ice ages. Although ice ages have some impacts that have been permanent, these are the cyclical climate dynamics that occur around the globe.

Land colonization
After the evolution of Earth, the colonization of land became a crucial factor in creating an ideal habitat for photographs and animals. Starting from the earliest Precambrian and Paleozoic periods, extra-simple life forms began to be more exposed in the old terrestrial world.
Today, there are some land plants, like bryophytes, that are starting to dwell on land. Plants underwent their evolutionary adaptation, which helped them diversify and, in turn, create the ecosystems that supported various kinds of animal life. There would have been no oxygen to breathe on Earth had it not been for the existence of plant life that releases oxygen during photosynthesis.
When it comes to the fauna, arthropods, as a group of creatures, were, of course, among the animals that made it onto the land. This is one of the amazing aspects of these creatures: they developed exoskeletons and jointed legs, which helped them charm in this habitat. And so, this adaptation provided the basic framework for land-dwelling creatures such as insects.Eventually vertebrates.
The relationship of mutual life also contributed to the colonization of land. In other words, chemical bonds existing between plants and pollinators helped plants reproduce, while herbivores depended on plants for feeding. These interactions further inspired the existence of ecosystems that, consequently, made our planet more sustainable.
Analyzing the aspects of land colonization lets us feel what is happening now with our planet. Building habitats on land for plants and animals meant that an ecosystem, which is rather complex and exists today, was created.

The Rise of Human Civilization
With the successive development of human civilization, we have seen the fabrication of tools, agriculture, technology, energy resources, and indoor water. Early humans learned how to use rocks and sticks as hunting and gathering tools. Tools assisted our forefathers to deal with everyday life, and ultimately, they forge pieces with metal, brass, and iron, whose quality becomes sophisticated with time.
Agriculture is the backbone of our society. It allowed for the development of society. During the so-called Neolithic Revolution, people moved from a rather mobile lifestyle to a sedentary one, and for the first time in human history, they became settled farmers. They were, in effect, borne by ancestors who changed from a hunting-gathering society to an agricultural one, thus planting crops and raising animals for food and supporting population growth.
Humans soon became successful farmers who were able to cultivate food, and this continued to nudge the evolution of human civilizations. This period was followed by the Bronze Era and the Iron Age, when significant progress took place. With the help of tools made of metal, people changed the way they worked on fields and building sites and consequently increased the efficiency of agricultural and construction work. Over time, people became better at recording their ideas by utilizing writing systems, which made it easier to move stuff around the space with the wheel, which also changed their lives.
In fact, it was when communities grew that energy became crucial. For earlier humans, forces of people, animals, and even windmills were used in the beginning; however, technological progress makes things increasingly smarter. But the emergence of the Industrial Revolution was all part of this, as it gave birth to the exploitation of fuels such as coal, oil, and gas. Further on in this demonstration, the scale of the seized opportunities greatly magnified the capabilities of the people, therefore evolving the lifestyle in urban areas, modernizing the transport systems, and increasing industries’ growth on a high level.
Management of resources such as water, crops, and cattle has always been a part of society. From the moment of existence, the basis of evolution and growth of societies is the natural resources such as water, minerals, and timber. The use of resources in such a prudent manner was found to be the basis for the prosperity of civilizations, while others met misfortune because of excessive resource mining, scarcity, bad decisions, or weak management.
Among the highlights of the history of civilization that are known to us are the adoption and responsible management of tools, farming, technology, energy sources, and nature endowments. This technology enabled and therefore stimulated the establishment and development of our society. Humans widened their span and achieved accomplishments that affected the creation of our current world.
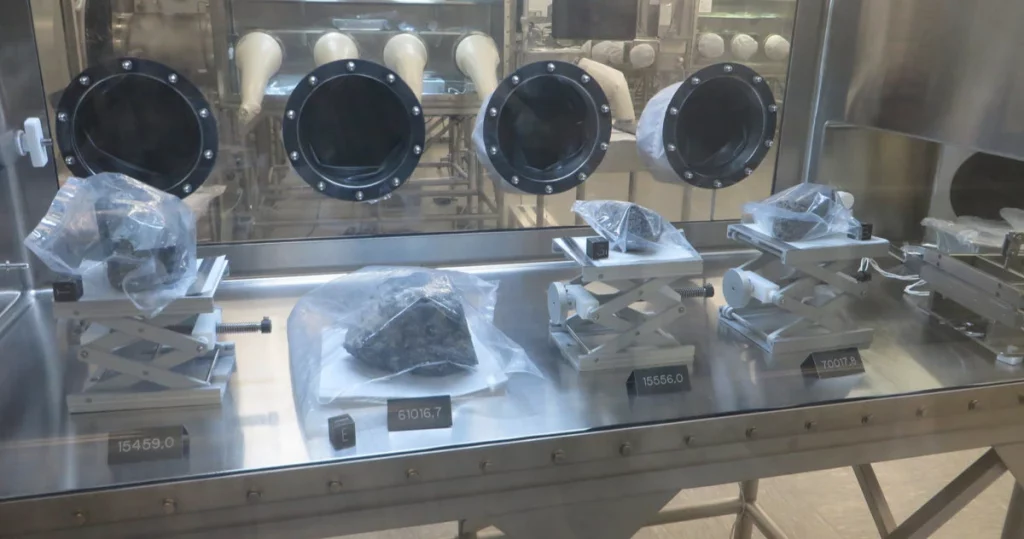

Scientific Research and Exploration
When we set out on a voyage to find the facts that helped our planet transform into a livable place, it is imperative to learn about the role of research and exploration. NASA stands out among all as it has pioneered most of this space exploration and earthly paleontological research, thus leading to new and exciting breakthroughs and a new understanding of the key events on our planet Earth.
Similarly, after many years of testing, scientists have created a time scale consisting of periods. These are times that chart the milestones in the evolutionary path of the planet, providing us with a history of the trail. Considering the span of time in your scientific investigation, it becomes essential to comprehend not only how Mother Nature works but also those fundamental events that have sculpted this world.
A substantial study tool in this type of research is the use of computer simulations. Models of Earth systems constructed in the labs enable a comprehensive understanding of the processes that took years and their remote effects. The combination of information from living things, climate, and rock formations assists you in generating and showing the impact that each of these events had on the planet.
There are creatures in this world that have been here throughout the planet’s history, and not just human beings; they all have a substantial role to play.Through mechanisms, species have. Such impacts caused various and immense changes to the environment, and these changes, which contain important clues about Earth’s development, are still changing today.
Exploring such life forms and how they shape the Earth will give us a better understanding of the history of the planet on which we live.
Successful coverage of this topic requires that you be confident and informed. With this trait, you can then proceed to dissect in great detail the 25 happenings that have been historical-changing events. Keep in mind preserving the objectivity of your research paper; utilize the evidence gathered through the research and exploration process. Being able to tell the story of the wondrous journey of the planet will be a result of the chosen method.
Looking Ahead
When you keep on peeling at the various milestones that have developed the planet, you should keep in mind the threats and possibilities that lie ahead. Know that what happens today will shape the future of Earth and ultimately bring about its fate.
Moreover, we struggle with climate change, which is one of the obstacles. It is so dangerous, not only for animals but also for many different plants. That is why some species may die out. To save the climate from the devastating consequences of climate change, we have to diminish greenhouse gas levels and increase renewable energy use. Together with this first part of the strategy, we must also handle the problems of species’ preservation, as today’s decisions will decide whether endangered animals and plants will survive in the future.
Space exploration can be understood as an instrumental tool for various scientific studies and the progress of human understanding of the cosmos. With every day that passes, we move closer to the future. During this time, take a moment to think about the new opportunities that may come up due to technical developments. The knowledge we register in space could lead to a determinant innovation that would improve our lives on Earth tremendously. In view of this, it paves the way for the development of creation.
Adressing the challenges of tomorrow requires a recognition of the multifaceted nature of some of them. As you navigate the maze of our world’s complexities, bear in mind the fact that the themes of climate change, species conservation, and a whole list of other urgent problems are complementary. By joining forces and appreciating others opinions, we will succeed together. This is the only way for us to secure a future that is sustainable for our children and those after them.
Whenever you are reminded of this, always bear in mind that our planet’s destiny is in your hands. Equipped with the knowledge of things that happened and possibly understanding what events are taking place in the world today, you are also able to make the world better. Trust your intuition and be aware that your actions can play a significant role in bringing about a planet with sustainable living conditions, justice, and general well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What were the significant events leading up, to Earths formation?
The story of the creation of our planet dates back 4.6 billion years, when the particles and gases of the nebula came together and originated the solar system where planet Earth was born. The heat of the earth was quite intense during its earlier stages; it progressively cooled down and had its surface solidify into a crust. Step by step, the slow cycles of heating and cooling have aided in the composition of the earth’s crust and the development of the atmosphere surrounding our planet.
Which mass extinctions had the impact, on life?
Over the span of Earth’s geological history, the planet has witnessed several major extinction events. The most influential extinction events include the Permian-Triassic and Cretaceous Paleogene events, which occurred around 252 and 62 million years ago, respectively. Such acts of cataclysm led to the extinction of up to 96% and 75% of all living things on Earth, respectively. Their effect is immutable and is what has guided civilization the way it is today.
What is the significance of the explosion in Earths history?
Signaling the origin of life on earth 541 million years ago, the Cambrian explosion bears the responsibility for speeding up the diversification and evolution of intricate life organisms. This period saw the growth and multiplication of a plethora of animal phyla that exist now. The rapid rise of biological diversity has greatly influenced our planet’s responsive systems. Create a path for a revolutionary leap in human advancement.
How did movements of plates shape Earths continents and oceans?
The types of motions a plate has caused on Earth have had an impact on the features on the continents and oceans through processes such as continental drift, seafloor spreading, and mountain building. With millions of years in their accounts, the Earth’s landmasses have undergone movements that have led to the continuous merging and separation of continents and the resultant changes in their arrangement and the formation of ocean basins.
What are some milestones in evolution that mark the development of life forms?
The evolution of many life forms on Earth was marked by several crucial developmental points. These include the emergence of cells (cyanobacteria) 2.5 billion years ago, the evolution of multicellularity 1.5–1 billion years ago, the development of sexual reproduction around 1 billion years ago, and the appearance of early animals approximately 900–600 million years ago.
How have human activities impacted changes?
Our world has been highly affected by human activities through the development of industries, agriculture, and deforestation. It is consequently to blame for consequences that do include climate change, habitat loss, and air and water resource pollution. They have already exacerbated greenhouse gas emissions, hence the rising global temperature, which poses a great threat to the environment.







